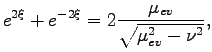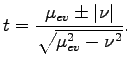Next: Bogolyubov transformation of the
Up: Canonical Hamiltonians for waves
Previous: Window transform
Calculation of 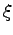
In order to calculate 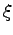 , we solve Eq. (79)
Notice that
, we solve Eq. (79)
Notice that
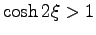 since
since
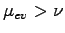 .
Using the definition of the
.
Using the definition of the 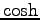 function, we can write
function, we can write
and denoting
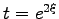 , one obtains a quadratic equation for
, one obtains a quadratic equation for 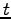 with two solutions
with two solutions
After we take into account Eq. (80), we obtain the following expression for 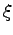
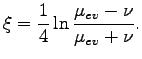 |
|
|
(91) |
Dr Yuri V Lvov
2008-07-08