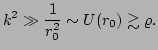Next: Strong condensate case
Up: Applicability of WKB descriptions
Previous: Applicability of WKB descriptions
Firstly, let us consider the case of a weak condensate so that the
effect of the nonlinear term is small in comparison to the linear
ones,
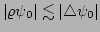 . Since
. Since 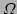 is a constant we observe that the Laplacian term acts to balance the
external potential term (like in the linear Schrödinger equation)
and the nonlinear term can be, at most, as big as the linear ones
where
is a constant we observe that the Laplacian term acts to balance the
external potential term (like in the linear Schrödinger equation)
and the nonlinear term can be, at most, as big as the linear ones
where 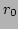 is the characteristic size of the condensate (it is defined
as the condensate `` reflection'' point via the condition
is the characteristic size of the condensate (it is defined
as the condensate `` reflection'' point via the condition
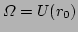 , see below).
, see below).
Now for a WKB description to be valid we require
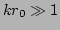 ,
i.e. we require the characteristic length-scale of our wavepackets to
be a lot smaller than that of the large-scales. Using this fact we
find
,
i.e. we require the characteristic length-scale of our wavepackets to
be a lot smaller than that of the large-scales. Using this fact we
find
Therefore, the condensate correction to the frequency, given by
(![[*]](file:/usr/share/latex2html/icons/crossref.png) ), is small. In other words the wavepacket
does not `` feel'' the condensate. Indeed, from
), is small. In other words the wavepacket
does not `` feel'' the condensate. Indeed, from
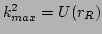 we have
we have
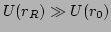 and this implies that
and this implies that
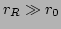 (where
(where 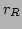 is the wavepacket reflection point, see
figure 2). Thus, the condensate in this case occupies a tiny space at
the bottom of the potential well and hence does not affect a
wavepacket's motion. Therefore, a wavepacket moves as a ``
classical'' particle described by the Ehrenfest equations
(
is the wavepacket reflection point, see
figure 2). Thus, the condensate in this case occupies a tiny space at
the bottom of the potential well and hence does not affect a
wavepacket's motion. Therefore, a wavepacket moves as a ``
classical'' particle described by the Ehrenfest equations
(![[*]](file:/usr/share/latex2html/icons/crossref.png) ) and (
) and (![[*]](file:/usr/share/latex2html/icons/crossref.png) ). In fact, in this case it would be
incorrect to try to describe the small condensate corrections via our
WKB approach because these corrections are of order
). In fact, in this case it would be
incorrect to try to describe the small condensate corrections via our
WKB approach because these corrections are of order
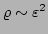 (the
(the
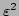 terms being ignored in a WKB
description).
terms being ignored in a WKB
description).



Next: Strong condensate case
Up: Applicability of WKB descriptions
Previous: Applicability of WKB descriptions
Dr Yuri V Lvov
2007-01-23
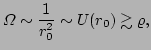
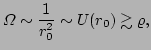
![]() ,
i.e. we require the characteristic length-scale of our wavepackets to
be a lot smaller than that of the large-scales. Using this fact we
find
,
i.e. we require the characteristic length-scale of our wavepackets to
be a lot smaller than that of the large-scales. Using this fact we
find